Probiotics and Prebiotics
Key Takeaways
- Probiotics are beneficial bacteria that support gut health.
- Prebiotics are non-digestible fibers that feed probiotics.
- Both are essential for a balanced digestive system.
- Incorporating a variety of sources can enhance digestive health.
- Consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new supplements.
Welcome to HealthyGutSolutions! In this article, we will explore the fascinating world of probiotics and prebiotics, their roles in digestive health, and how you can incorporate them into your diet for overall wellness.
Understanding Probiotics
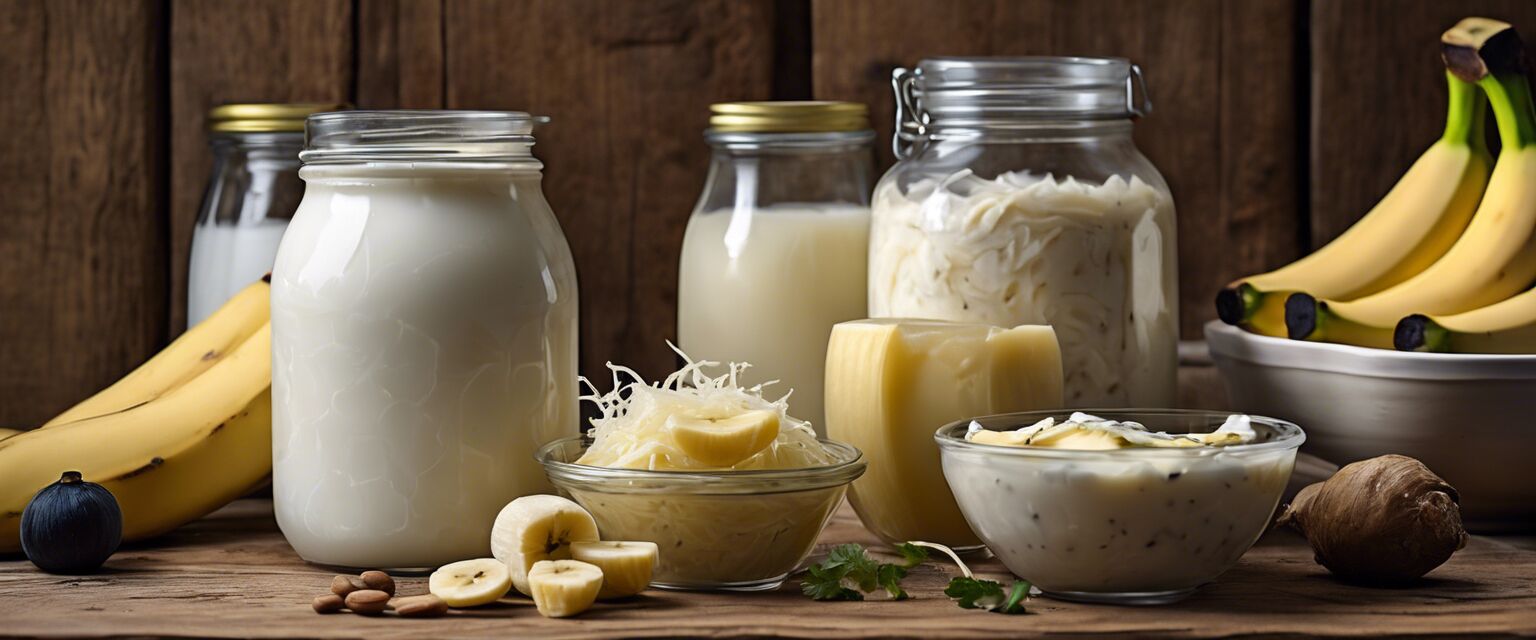
Probiotics are live microorganisms, often referred to as "good" bacteria, that provide numerous benefits to the digestive system. These beneficial microbes can help maintain a balanced gut microbiota, which is crucial for digestive health.
Sources of Probiotics
| Source | Description |
|---|---|
| Yogurt | Fermented dairy product rich in live cultures. |
| Kefir | A fermented drink made from milk or water, containing various bacteria and yeasts. |
| Sauerkraut | Fermented cabbage that is high in probiotics and nutrients. |
| Kombucha | A fermented tea beverage that contains live cultures. |
| Miso | A fermented soybean paste used in soups and seasoning. |
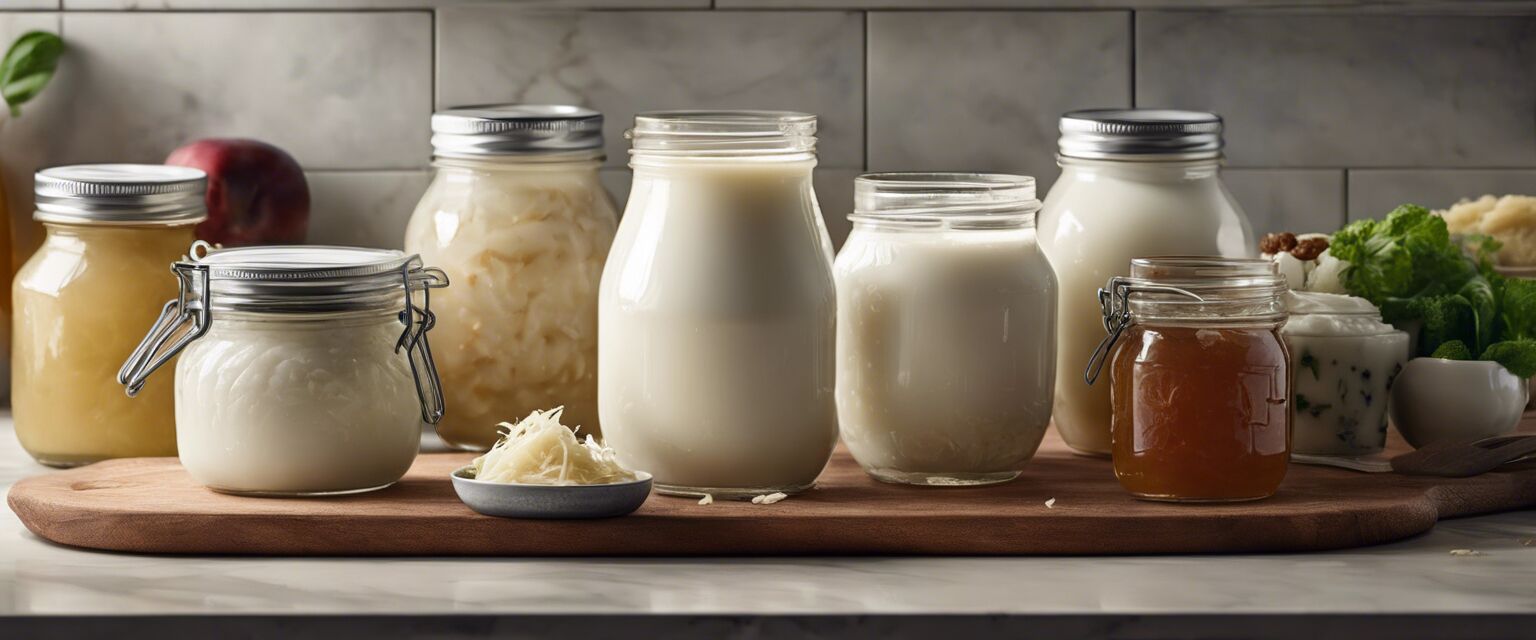

Understanding Prebiotics
Prebiotics are a type of non-digestible fiber that serves as food for probiotics. By consuming prebiotics, you can help support the growth and activity of good bacteria in your gut.
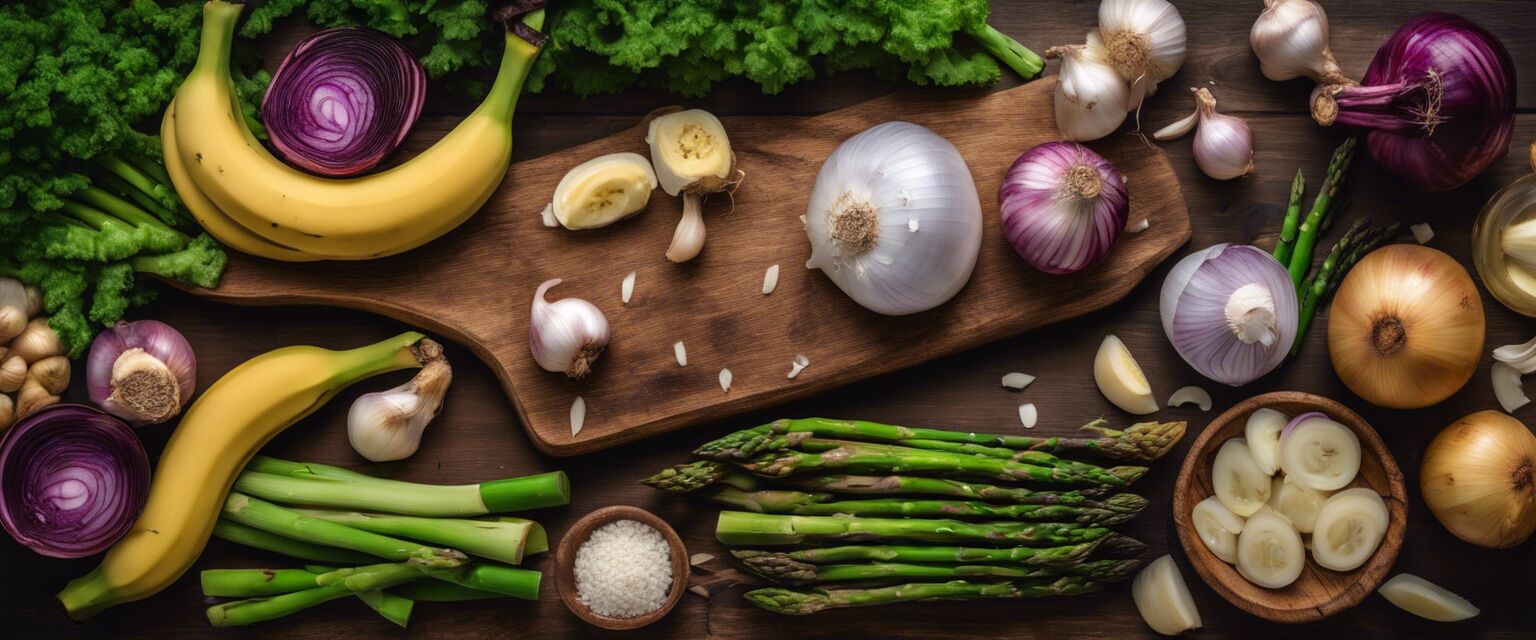
Sources of Prebiotics
| Source | Description |
|---|---|
| Bananas | Rich in inulin, a type of prebiotic fiber. |
| Garlic | Contains fructooligosaccharides, which promote beneficial gut bacteria. |
| Onions | A good source of prebiotic fibers that aid digestion. |
| Asparagus | Contains inulin and other prebiotics beneficial for gut health. |
| Chicory Root | One of the richest sources of inulin, often used as a dietary supplement. |

The Importance of the Gut Microbiome
The gut microbiome is a complex community of microorganisms residing in our digestive system. A balanced gut microbiome is essential for various bodily functions, including digestion, immune response, and even mood regulation.
How Probiotics and Prebiotics Work Together
Probiotics and prebiotics work synergistically to support gut health. While probiotics introduce beneficial bacteria into your system, prebiotics provide the necessary nutrients for these bacteria to thrive.
Incorporating Probiotics and Prebiotics into Your Diet
To reap the benefits of probiotics and prebiotics, consider the following tips:
Tips for Beginners
- Start your day with a serving of yogurt or kefir.
- Include garlic and onions in your cooking for added flavor and health benefits.
- Snack on bananas or prebiotic-rich snacks throughout the day.
- Experiment with fermented foods like sauerkraut and kombucha.
- Gradually increase your intake to allow your digestive system to adjust.
Potential Benefits of Probiotics and Prebiotics
While research is ongoing, some potential benefits associated with probiotics and prebiotics include:
- Support for healthy digestion
- Boosted immune system
- Improved gut health
- Enhanced nutrient absorption
- Possible mood regulation
Pros and Cons of Probiotics and Prebiotics
Pros
- Promotes a balanced gut microbiome.
- Supports digestive health.
- May enhance immune function.
- Available in various food sources and supplements.
Cons
- Some people may experience digestive discomfort.
- Quality of supplements can vary.
- Not all strains are beneficial for every individual.
- Consultation with a healthcare professional is recommended.
Conclusion
Probiotics and prebiotics are vital components of a healthy diet, contributing to digestive health and overall wellness. By incorporating a variety of sources into your meals, you can support your gut microbiome and enhance your health. Always remember to consult with a healthcare professional before making significant changes to your diet or starting new supplements.
For more information on related topics, explore our other articles on probiotics and prebiotics, digestive enzymes, and fiber supplements. Discover how these products can contribute to your digestive health journey!